VITEEE EXAM 2016 - Question Paper with Solutions
Viteee exam is online for BTech programmes in VIT University. It is compulsory to write the viteee exam to get admission in VIT University. So I'm giving Viteee exam 2016 previous year chemistry question paper with solutions to prepare for the exam. Download viteee exam 2016 previous year chemistry question paper with solution
To get admission in VIT UNIVERSITY for all the campuses (Vellore, Chennai, Bhopal, Amaravati), students need to clear the VITEEE EXAM, that's one of the toughest exams to enter into VIT University in associate country, VITEEE Exam 2016 previous year question papers with solutions will help students to rearrange for the examination.
Also Read
VITEEE Exam 2016 - Question paper with solutions (Part 1)
VITEEE Exam 2016 - Question paper with Solutions (Part 3)
VITEEE Exam 2019 - Previous year question paper, sample paper, mock test, syllabus
Download link will be available below
So in this post, I will give you the VITEEE EXAM 2016 chemistry question paper with solutions. There will be 40 questions out of 120 questions. Correct answer and explanation for each question are available after each question and answer. Download links for VITEEE EXAM 2016 question paper will be available at the end of the page. Prepare well and Don't leave any questions.
I'm also a student and I know how hard it is to get admission and pass the online entrance exam. So that's why I'm giving you the Previous year question paper with solutions to easily pass the VITEEE EXAM.
VITEEE EXAM 2016 - Question Paper with Solutions (Part 2)
41. Among the elements Ca, Mg, P and Cl, the order of increasing atomic radii is
A) Mg < Ca < Cl < P
B) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
C) P < Cl < Ca < Mg
D) Ca < Mg < P < Cl
A) Mg < Ca < Cl < P
B) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
C) P < Cl < Ca < Mg
D) Ca < Mg < P < Cl
Answer: B) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
Explanation: With an increase in the number of electrons in the same shell, the atomic radii decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. However, atomic radii increases, as the number of shells increases. Thus, on moving down a group atomic radii increases. The electronic configuration of the given element is Mg12 = [Ne] 3s² Ca20 = [Ar] 4s² P15 = [Ne] 3s²3p³ Cl17 = [Ne] 3s²3p5 In Mg, P and Cl, the number of electrons is increasing in the same shell, thus the order of their atomic radii is Cl < P < Mg In Ca, the electron is entering in higher shell, thus, it has the highest atomic radii among the given. Thus, the order of radii is Cl < P < Mg < Ca
42. The reaction, 2A (g) + B (g) ⇌ 3C (g) + D (g) is begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression
A) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(1.00)² (1.00)]
B) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.50)² (0.75)]
C) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.50)² (0.25)]
D) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.75)² (0.25)]
Explanation: With an increase in the number of electrons in the same shell, the atomic radii decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. However, atomic radii increases, as the number of shells increases. Thus, on moving down a group atomic radii increases. The electronic configuration of the given element is Mg12 = [Ne] 3s² Ca20 = [Ar] 4s² P15 = [Ne] 3s²3p³ Cl17 = [Ne] 3s²3p5 In Mg, P and Cl, the number of electrons is increasing in the same shell, thus the order of their atomic radii is Cl < P < Mg In Ca, the electron is entering in higher shell, thus, it has the highest atomic radii among the given. Thus, the order of radii is Cl < P < Mg < Ca
42. The reaction, 2A (g) + B (g) ⇌ 3C (g) + D (g) is begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression
A) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(1.00)² (1.00)]
B) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.50)² (0.75)]
C) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.50)² (0.25)]
D) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.75)² (0.25)]
Answer: B) [(0.75)³ (0.25)] / [(0.50)² (0.75)]
Explanation:
Explanation:
43. Which of the following expressions correctly represents, the equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of Al₂ (SO₄)₃? Given that ∧° Al3+ and ∧°SO2- ₄ are the equivalent conductances at infinite dilution of the respective ions?
A) 2∧° Al3+ + 3∧° SO2-₄
B) ∧° Al3+ + ∧° SO2-₄
C) (∧° Al3+ + 3∧° SO2-₄) * 6
D) 1/3 ∧° Al3+ + 1/2 ∧° SO2-₄
A) 2∧° Al3+ + 3∧° SO2-₄
B) ∧° Al3+ + ∧° SO2-₄
C) (∧° Al3+ + 3∧° SO2-₄) * 6
D) 1/3 ∧° Al3+ + 1/2 ∧° SO2-₄
Answer: B) ∧° Al3+ + ∧° SO2-₄
Explanation: Al₂ (SO₄)₃ ⇌ 2Al3+ + 3SO2- ₄ since equivalent conductance are given only for ions, the equivalent conductance at infinite dilution, ∧∞ eq = ∧ ° Al3+ + ∧° SO2- ₄
44. The pressure exerted by 6.0g of methane gas in a 0.03 m³ vessel at 129°C is (Atomic masses: C = 12.01, H = 1.01 and R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
A) 215216 Pa
B) 13409 Pa
C) 41648 Pa
D) 31684 Pa
Explanation: Al₂ (SO₄)₃ ⇌ 2Al3+ + 3SO2- ₄ since equivalent conductance are given only for ions, the equivalent conductance at infinite dilution, ∧∞ eq = ∧ ° Al3+ + ∧° SO2- ₄
44. The pressure exerted by 6.0g of methane gas in a 0.03 m³ vessel at 129°C is (Atomic masses: C = 12.01, H = 1.01 and R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
A) 215216 Pa
B) 13409 Pa
C) 41648 Pa
D) 31684 Pa
Answer: C) 41648 Pa
Explanation: Given, volume, V = 0.03 m³ temperature, T = 129 + 273 = 402 K mass of methane, W = 6.0 g mol mass of methane, M = 12.01 + 4 * 1.01 = 16.05 from, ideal gas equation, pV = nRT p = 6 / 16.05 * 8.314 * 402 / 0.03 = 41648 Pa
45. Match List I (Equations) with List-II (Types of a process) and select the correct option.
List-I Equations
A. KP > Q
B. ΔG° < RT 1n Q
C. KP = Q
D. T > ΔH / ΔS
List-II Types of process
1. Non-spontaneous
2. Equilibrium
3. Spontaneous and endothermic
4. Spontaneous
A) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Explanation: Given, volume, V = 0.03 m³ temperature, T = 129 + 273 = 402 K mass of methane, W = 6.0 g mol mass of methane, M = 12.01 + 4 * 1.01 = 16.05 from, ideal gas equation, pV = nRT p = 6 / 16.05 * 8.314 * 402 / 0.03 = 41648 Pa
45. Match List I (Equations) with List-II (Types of a process) and select the correct option.
List-I Equations
A. KP > Q
B. ΔG° < RT 1n Q
C. KP = Q
D. T > ΔH / ΔS
List-II Types of process
1. Non-spontaneous
2. Equilibrium
3. Spontaneous and endothermic
4. Spontaneous
A) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Answer: C) A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
Explanation: (A) When KP > Q, the reaction goes in forward direction, i.e., the reaction is spontaneous. (B) Given, ΔG° < RT 1n Q, thus, ΔG° = +ve and hence, the reaction is non-spontaneous. (C) At equilibrium, KP = Q (D) T > ΔH / ΔS or TΔS > ΔH this condition is true for spontaneous endothermic reactions (as ΔG ≥ ΔH - TΔS)
46. Among the following which one has the highest cation of anion size ratio?
A) CsI
B) CsF
C) LiF
D) NaF
Answer: B) CsFExplanation: (A) When KP > Q, the reaction goes in forward direction, i.e., the reaction is spontaneous. (B) Given, ΔG° < RT 1n Q, thus, ΔG° = +ve and hence, the reaction is non-spontaneous. (C) At equilibrium, KP = Q (D) T > ΔH / ΔS or TΔS > ΔH this condition is true for spontaneous endothermic reactions (as ΔG ≥ ΔH - TΔS)
46. Among the following which one has the highest cation of anion size ratio?
A) CsI
B) CsF
C) LiF
D) NaF
Explanation: The order of the size of given cations is Li+ < Na+ < Cs+ and the order of the size of given anions is I- > F- Thus when the cation is largest and the anion is smallest, the cation to anion size ratio is maximum. Hence, cation to anion size ratio is maximum for CsF.
47. Which of the following species is not electrophilic in nature?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: A) A
Explanation: Electrophiles are electron deficient species. Among the given H₃O⊕ has lone pair of electrons for donation, thus it is not electron deficient and hence, does not behave like an electrophile.
48. Match List I (Substances) with List-II (Processes employed in the manufacture of the substances) and select the correct option.
List-I Substances
A.Sulphuric acid
B.Steel
C.Sodium hydroxide
D.Ammonia
List-II Processes
1.Haber's process
2.Bessemer's process
3.Leblanc process
4.contact process
A) A-1, B-4, C-2, D-3
B) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
C) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
D) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
Explanation: Electrophiles are electron deficient species. Among the given H₃O⊕ has lone pair of electrons for donation, thus it is not electron deficient and hence, does not behave like an electrophile.
48. Match List I (Substances) with List-II (Processes employed in the manufacture of the substances) and select the correct option.
List-I Substances
A.Sulphuric acid
B.Steel
C.Sodium hydroxide
D.Ammonia
List-II Processes
1.Haber's process
2.Bessemer's process
3.Leblanc process
4.contact process
A) A-1, B-4, C-2, D-3
B) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
C) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
D) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
Answer: C) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
Explanation: Sulphuric acid is manufactured by contact process, steel is manufactured by Bessemer's process, the Leblanc process is used for the production of NaOH while NH₃ is obtained by Haber' process.
49. When glycerol is treated with an excess of HI, it produces
A) 2-iodopropane
B) allyl iodide
C) propene
D) glycerol triiodide
Explanation: Sulphuric acid is manufactured by contact process, steel is manufactured by Bessemer's process, the Leblanc process is used for the production of NaOH while NH₃ is obtained by Haber' process.
49. When glycerol is treated with an excess of HI, it produces
A) 2-iodopropane
B) allyl iodide
C) propene
D) glycerol triiodide
Answer: B) allyl iodide
Explanation:
50. Some statements about heavy water are given below. (i) Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors (ii) Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water (iii) Heavy water is more effective solvent than ordinary water Which of the above statements are correct?
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i), (ii) and (iii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i) and (iii)
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i), (ii) and (iii)
C) (ii) and (iii)
D) (i) and (iii)
Answer: A) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors. Its boiling point is higher as compared to ordinary water. Thus, it is more associated as compared to ordinary water. The dielectric constant is however higher for H₂O, thus, H₂O is a more effective solvent than heavy water (D₂ O).
51. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated?
Explanation: Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors. Its boiling point is higher as compared to ordinary water. Thus, it is more associated as compared to ordinary water. The dielectric constant is however higher for H₂O, thus, H₂O is a more effective solvent than heavy water (D₂ O).
51. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: C) C
Explanation: Dehydration of alcohols involves the formation of carbocation intermediate. More the stability of carbocation, higher is the ease of dehydration. The order of stability of carbocation, given by the given compound is given above.
Explanation: Dehydration of alcohols involves the formation of carbocation intermediate. More the stability of carbocation, higher is the ease of dehydration. The order of stability of carbocation, given by the given compound is given above.
52. Which one of the following complexes is not expected to exhibit isomerism?
A) [Ni (NH₃)₄(H₂O) ₂]2+
B) [Pt (NH₃)₂Cl₂]
C) [Ni (NH₃)₂Cl₂]
D) [Ni (en) ₃]2+
A) [Ni (NH₃)₄(H₂O) ₂]2+
B) [Pt (NH₃)₂Cl₂]
C) [Ni (NH₃)₂Cl₂]
D) [Ni (en) ₃]2+
Answer: C) [Ni (NH₃)₂Cl₂]
Explanation: [Ni (NH₃)₂Cl₂] has tetrahedral geometry and thus, does not exhibit isomerism due to the presence of symmetry elements.
53. Which of the following conformers for ethylene glycol is most stable?
Explanation: [Ni (NH₃)₂Cl₂] has tetrahedral geometry and thus, does not exhibit isomerism due to the presence of symmetry elements.
53. Which of the following conformers for ethylene glycol is most stable?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: D) D
Explanation:
Explanation:
54. The IUPAC name of the compound CH₃CH = CHC ≡ CH is
A) pent-4-yn-2-ene
B) pent-3-en-1-yne
C) pent-2-en-4-yne
D) pent-l-yn-3-ene
A) pent-4-yn-2-ene
B) pent-3-en-1-yne
C) pent-2-en-4-yne
D) pent-l-yn-3-ene
Answer: B) pent-3-en-1-yne
Explanation:
Explanation:
55. Which of the following oxidation states is the most common among the lanthanoids?
A) 4
B) 2
C) 5
D) 3
A) 4
B) 2
C) 5
D) 3
Answer: D) 3
Explanation: The most common oxidation state exhibited by lanthanoids is +3.
56. Some of the properties of the two species, NO- ₃ and H₃O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct?
A) Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures
B) Isostructural with the same hybridization for the central atom
C) Isostructural with different hybridization for the central atom
D) Similar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures
Explanation: The most common oxidation state exhibited by lanthanoids is +3.
56. Some of the properties of the two species, NO- ₃ and H₃O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct?
A) Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures
B) Isostructural with the same hybridization for the central atom
C) Isostructural with different hybridization for the central atom
D) Similar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures
Answer: A) Dissimilar in hybridization for the central atom with different structures
Explanation:
Explanation:
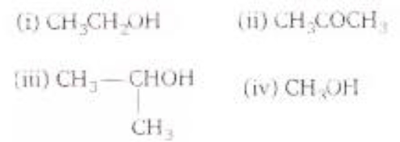
57. Which of the below compounds on being warmed with iodine solution and NaOH, will give iodoform?
A) (i), (iii) and (iv)
B) Only (ii)
C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
D) (i) and (ii)
Answer: C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation:
Explanation:
58. Fructose reduces Tollen's reagent due to
A) asymmetric carbons
B) primary alcoholic group
C) secondary alcoholic group
D) enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to the aldehyde by the base
A) asymmetric carbons
B) primary alcoholic group
C) secondary alcoholic group
D) enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to the aldehyde by the base
Answer: D) enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to the aldehyde by the base
Explanation: In aqueous solution. Fructose is enolised and then converted into aldehyde in basic medium. All aldehydes generally reduce Tollen's reagent, thus fructose also reduces Tollen's reagent.
59. In the following reaction,
Explanation: In aqueous solution. Fructose is enolised and then converted into aldehyde in basic medium. All aldehydes generally reduce Tollen's reagent, thus fructose also reduces Tollen's reagent.
59. In the following reaction,
A) C6H5CH₂OCH₂C6H5
B) C6H5CH₂OH
C) C6H5CH₃
D) C6H5CH₂CH₂C6H5
Answer: C) C6H5CH₃
Explanation:
Explanation:
60. Which of the following is not a fat soluble vitamin?
A) Vitamin-B complex
B) Vitamin-D
C) Vitamin-E
D) Vitamin-A
A) Vitamin-B complex
B) Vitamin-D
C) Vitamin-E
D) Vitamin-A
Answer: A) Vitamin-B complex
Explanation: Vitamin - A, D and E are fat soluble vitamins, whereas vitamin-B complex is a water-soluble vitamin.
61. Which of the statements about 'Denaturation' given below is correct?
Statements (i) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(ii) Denaturation! Leads to the conversion of a double strand of DNA into a single strand.
(iii) Denaturation affects primary structure which gets destroyed.
A) (ii) and (iii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (i) and (ii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Vitamin - A, D and E are fat soluble vitamins, whereas vitamin-B complex is a water-soluble vitamin.
61. Which of the statements about 'Denaturation' given below is correct?
Statements (i) Denaturation of proteins causes loss of secondary and tertiary structures of the protein.
(ii) Denaturation! Leads to the conversion of a double strand of DNA into a single strand.
(iii) Denaturation affects primary structure which gets destroyed.
A) (ii) and (iii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (i) and (ii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer: C) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: During denaturation secondary and tertiary structures of protein destroyed but the primary structure remains intact. Heat, acid and alkali denature DNA molecule and a double strand of DNA converts into a single strand.
62. Which has the maximum number of molecules among the following?
A) 44 g CO₂
B) 48 g O₃
C) 8 g H₂
D) 64 g SO₂
Explanation: During denaturation secondary and tertiary structures of protein destroyed but the primary structure remains intact. Heat, acid and alkali denature DNA molecule and a double strand of DNA converts into a single strand.
62. Which has the maximum number of molecules among the following?
A) 44 g CO₂
B) 48 g O₃
C) 8 g H₂
D) 64 g SO₂
Answer: C) 8 g H₂
Explanation: 44 g CO₂ = 1 mol CO₂ = N A molecules of CO₂ 48 g O₃ = 1 mol O₃ = N A molecules of O₃ 8 g H₂ = 4 mol H₂ = 4 * N A molecules of H₂ 64 g SO₂ = 1 mol SO₂ = N A molecules of SO₂
63. Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily?
Explanation: 44 g CO₂ = 1 mol CO₂ = N A molecules of CO₂ 48 g O₃ = 1 mol O₃ = N A molecules of O₃ 8 g H₂ = 4 mol H₂ = 4 * N A molecules of H₂ 64 g SO₂ = 1 mol SO₂ = N A molecules of SO₂
63. Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: A) A
Explanation:
Explanation:
64. A 0.1 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid is 30% ionized. If Kƒ for water is 1.86°C/m, the freezing point of the solution will be
A) - 0.18°C
B) - 0.54°C
C) - 0.36°C
D) - 0.24°C
A) - 0.18°C
B) - 0.54°C
C) - 0.36°C
D) - 0.24°C
Answer: D) - 0.24°C
Explanation: Freezing point depression (ΔTƒ) = iKƒm HA → H+ + A- 1 - α α α 1 - 0.3 0.3 0.3 i = 1 - 0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3 i = 1.3 ∴ ΔTƒ = 1.3 * 1.86 * 0.1 = 0.2418°C Tƒ = 0 - 0.2418°C = - 0.2418°C
65. Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest C - O bond?
A) Mn (CO) + 6
B) Cr (CO) 6
C) V (CO) - 6
D) Fe (CO) 5
Explanation: Freezing point depression (ΔTƒ) = iKƒm HA → H+ + A- 1 - α α α 1 - 0.3 0.3 0.3 i = 1 - 0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3 i = 1.3 ∴ ΔTƒ = 1.3 * 1.86 * 0.1 = 0.2418°C Tƒ = 0 - 0.2418°C = - 0.2418°C
65. Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest C - O bond?
A) Mn (CO) + 6
B) Cr (CO) 6
C) V (CO) - 6
D) Fe (CO) 5
Answer: A) Mn(CO)+ 6
Explanation: As a positive charge on the central metal atom increases, the less readily the metal can denote electron density into the anti-bonding π-orbitals of CO ligand to weaken the C - O bond. Hence, the C - O bond would be strongest in Mn (CO) + 6
66. The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) with the following compounds
Explanation: As a positive charge on the central metal atom increases, the less readily the metal can denote electron density into the anti-bonding π-orbitals of CO ligand to weaken the C - O bond. Hence, the C - O bond would be strongest in Mn (CO) + 6
66. The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) with the following compounds
A) III > II > I
B) II > I > III
C) I > III > II
D) I > II > II
Answer: D) I > II > III
Explanation: Since the alkyl group has +I-effect and aryl group has +R-effect, thus greater the number of alkyl and aryl groups attached to the carbonyl group, its reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction. Secondly, as the steric crowding on carbonyl group increases, the reactivity decreases accordingly.
So, the correct reactivity order for reaction with PhMgBr is what given above.
Explanation: Since the alkyl group has +I-effect and aryl group has +R-effect, thus greater the number of alkyl and aryl groups attached to the carbonyl group, its reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction. Secondly, as the steric crowding on carbonyl group increases, the reactivity decreases accordingly.
So, the correct reactivity order for reaction with PhMgBr is what given above.
67. A solid compound XY has a NaCl structure. If the radius of the cation is 100 pm, the radius of the anion (Y-) will be
A) 275.1 pm
B) 322.5 pm
C) 241.5 pm
D) 165.7 pm
A) 275.1 pm
B) 322.5 pm
C) 241.5 pm
D) 165.7 pm
Answer: C) 241.5 pm
Explanation: Radius ratio of NaCl like crystal = r+ / r- = 0.414 or r- = 100 / 0.414 = 241.5 pm
68. Consider the following processes ΔH(kJ/mol) 1/2 A → B + 150 3B → 2C + D - 125 E + A → 2D + 350 For B + D → E + 2C , ΔH will be
A) 525 kJ/mol
B) -175 kJ/mol
C) -325kJ/mol
D) 325 kJ/mol
Explanation: Radius ratio of NaCl like crystal = r+ / r- = 0.414 or r- = 100 / 0.414 = 241.5 pm
68. Consider the following processes ΔH(kJ/mol) 1/2 A → B + 150 3B → 2C + D - 125 E + A → 2D + 350 For B + D → E + 2C , ΔH will be
A) 525 kJ/mol
B) -175 kJ/mol
C) -325kJ/mol
D) 325 kJ/mol
Answer: B) -175 kJ/mol
Explanation: 1/2 A → B; ΔH = 150KJ/mol ...(i) 3B → 2C + D; ΔH = -125kJ/mol ...(ii) E + A → 2D; ΔH = +350kJ/mol ...(iii) By [2 * (i) + (ii)] - (iii), we have B + D → E + 2C ∴ ΔH = 150 * 2 + (-125) - 350 = -175 kJ/mol
69. Match the compounds given in List I with List II and select the suitable option using the codes given below.
List-I
A. Benz aldehyde
B. Phthalic anhydride
C. Phenyl benzoate
D. Methyl salicylate
List-II
1.Phenolphthalein
2.Benzon condensation
3.Oil of wintergreen
4.Fries rearrangement
A) A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
B) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
C) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Explanation: 1/2 A → B; ΔH = 150KJ/mol ...(i) 3B → 2C + D; ΔH = -125kJ/mol ...(ii) E + A → 2D; ΔH = +350kJ/mol ...(iii) By [2 * (i) + (ii)] - (iii), we have B + D → E + 2C ∴ ΔH = 150 * 2 + (-125) - 350 = -175 kJ/mol
69. Match the compounds given in List I with List II and select the suitable option using the codes given below.
List-I
A. Benz aldehyde
B. Phthalic anhydride
C. Phenyl benzoate
D. Methyl salicylate
List-II
1.Phenolphthalein
2.Benzon condensation
3.Oil of wintergreen
4.Fries rearrangement
A) A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
B) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
C) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Answer: D) A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: B) B
Explanation: Compound is most basic due to localized lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom while in other compounds, as a result of resonance, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom gets delocalized over benzene ring and thus is less easily available for donation.
Explanation: Compound is most basic due to localized lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom while in other compounds, as a result of resonance, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom gets delocalized over benzene ring and thus is less easily available for donation.
71. which of the following structures is the most preferred and hence of lowest energy for SO₃?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Answer: C) C
72. What is the value of electron gain enthalpy of Na+ if IE₁ of Na = 5.1 eV?
A) -5.1 eV
B) -10.2 eV
C) +2.55 eV
D) +10.2 eV
Answer: A) -5.1 eV
Explanation: IE₁ of Na = - Electron gain enthalpy of Na+ ion = -5.1 eV.
73. The unit of the rate constant for a zero-order reaction is
A) mol L-1 s-1
B) L mol-1 s-1
C) L² mol-2 s-1
D) s-1
Explanation: IE₁ of Na = - Electron gain enthalpy of Na+ ion = -5.1 eV.
73. The unit of the rate constant for a zero-order reaction is
A) mol L-1 s-1
B) L mol-1 s-1
C) L² mol-2 s-1
D) s-1
Answer: A) mol L-1 s-1
Explanation: For zero order reaction, Rate = k [Reactants] 0 ∴ Rate = k and unit of k = mol L-1 s-1
74. A bubble of air is underwater at temperature 15°C and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is 25°C and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
A) Volume will become greater by a factor of 1.6
B) Volume will become greater by a factor of 1.1
C) Volume will become smaller by a factor of 0.70
D) Volume will become greater by a factor of 2.9
Explanation: For zero order reaction, Rate = k [Reactants] 0 ∴ Rate = k and unit of k = mol L-1 s-1
74. A bubble of air is underwater at temperature 15°C and the pressure 1.5 bar. If the bubble rises to the surface where the temperature is 25°C and the pressure is 1.0 bar, what will happen to the volume of the bubble?
A) Volume will become greater by a factor of 1.6
B) Volume will become greater by a factor of 1.1
C) Volume will become smaller by a factor of 0.70
D) Volume will become greater by a factor of 2.9
Answer: A) Volume will become greater by a factor of 1.6
Explanation: ∴ p₁V₁ / T₁ = p₂V₂ / T₂ (By ideal gas equation) or 1.5 * V₁ / 288 = 1 * V₂ / 298 ∴ V₂ = 1.55 V₁ i.e., volume of bubble will be almost 1.6 times to initial volume of bubble.
75. Match List I with List II for the compositions of substances and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I Substances
A. Plaster of Paris
B. Epsomite
C. Kieserite
D. Gypsum
List-II Composition
1.CaSO₄ ⋅ 2H₂O
2.CaSO₄ ⋅ 1/2H₂O
3.MgSO₄ ⋅ 7H₂O
4.MgSO₄ ⋅ H₂O
5.CaSO₄
A) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
B) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
C) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-5
D) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
Explanation: ∴ p₁V₁ / T₁ = p₂V₂ / T₂ (By ideal gas equation) or 1.5 * V₁ / 288 = 1 * V₂ / 298 ∴ V₂ = 1.55 V₁ i.e., volume of bubble will be almost 1.6 times to initial volume of bubble.
75. Match List I with List II for the compositions of substances and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I Substances
A. Plaster of Paris
B. Epsomite
C. Kieserite
D. Gypsum
List-II Composition
1.CaSO₄ ⋅ 2H₂O
2.CaSO₄ ⋅ 1/2H₂O
3.MgSO₄ ⋅ 7H₂O
4.MgSO₄ ⋅ H₂O
5.CaSO₄
A) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
B) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
C) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-5
D) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
Answer: B) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
Explanation: (A) Plaster of Paris = CaSO₄ ⋅ 1/2H₂O (B) Epsomite = MgSO₄ ⋅ 7H₂O (C) Kieserite = MgSO₄ ⋅ H₂O (D) Gypsum = CaSO₄ ⋅ 2H₂O
76. The pairs of species of oxygen and their magnetic behaviours are noted below. Which of the following presents the correct description?
A) O- ₂ , O2- ₂ - Both diamagnetic
B) O+ , O2- ₂ - Both paramagnetic
C) O+ ₂ , O₂ - Both paramagnetic
D) O , O2- ₂ - Both paramagnetic
Explanation: (A) Plaster of Paris = CaSO₄ ⋅ 1/2H₂O (B) Epsomite = MgSO₄ ⋅ 7H₂O (C) Kieserite = MgSO₄ ⋅ H₂O (D) Gypsum = CaSO₄ ⋅ 2H₂O
76. The pairs of species of oxygen and their magnetic behaviours are noted below. Which of the following presents the correct description?
A) O- ₂ , O2- ₂ - Both diamagnetic
B) O+ , O2- ₂ - Both paramagnetic
C) O+ ₂ , O₂ - Both paramagnetic
D) O , O2- ₂ - Both paramagnetic
Answer: C) O+ ₂, O₂ - Both paramagnetic
Answer: A) SN 1 and SN 2
Explanation: C₂H5OH being a weaker nucleophile, when used as a solvent in case of hindered 1° halide, favours SN 1 mechanism while C₂H5O- being a strong nucleophile in this reaction favours SN 2 mechanism.
78. Which of the following complex compounds will exhibit highest paramagnetic behavior? (At.no. Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27, Zn = 30)
A) [Ti (NH₃)6]3+
B) [Cr (NH₃)6]3+
C) [Co (NH₃)6]3+
D) [Zn (NH₃)6]2+
Explanation: C₂H5OH being a weaker nucleophile, when used as a solvent in case of hindered 1° halide, favours SN 1 mechanism while C₂H5O- being a strong nucleophile in this reaction favours SN 2 mechanism.
78. Which of the following complex compounds will exhibit highest paramagnetic behavior? (At.no. Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27, Zn = 30)
A) [Ti (NH₃)6]3+
B) [Cr (NH₃)6]3+
C) [Co (NH₃)6]3+
D) [Zn (NH₃)6]2+
Answer: B) [Cr (NH₃)6]3+
79. Which of the following oxide is amphoteric?
A) SnO₂
B) CaO
C) SiO₂
D) CO₂
Answer: A) SnO₂
80. The following reactions take place in the blast furnace in the preparation of impure iron. Identify the reaction pertaining to the formation of the slag.
A) Fe₂O₃(s) + 3CO (g) → 2Fe (l) + 3CO₂ (g)
B) CaCO₃(s) → CaO(s) + CO₂ (g)
C) CaO(s) + SiO₂(s) → CaSiO₃(s)
D) 2C(s) + O₂ (g) → 2CO (g)
Explanation: A slag is an easily fusible material which is formed when gangue still present in the roasted or the calcined ore combines with the flux. For example, in the metallurgy of iron, CaO (flux) combines with silica gangue to form easily fusible calcium silicate (CaSiO₃) slag. CaO + SiO₂ → CaSiO₃ (slag)
ALL THE BEST!
Also Read
VITEEE Exam 2016 - Question paper with solutions (Part 1)
VITEEE Exam 2016 - Question paper with Solutions (Part 3)
VITEEE Exam 2019 - Previous year question paper, sample paper, mock test, syllabus
Keywords
viteee 2016 previous year papers, viteee previous year papers, vit previous year papers, viteee, which type of questions are asked in viteee, question papers, viteee papers, mock tests, viteee, viteee important question



























No comments